Identify Stakeholders
Identify Stakeholders
Project Integration Management is the specific responsibility of the project manager andit cannot be delegated or transferred. The project manager is the one that combines theresults from all the other Knowledge Areas to provide an overall view of the project. Theproject manager is ultimately responsible for the project as a whole.●Projects and project management are integrative by nature, with most tasks involvingmore than one Knowledge Area.●The relationships of processes within the Project Management Process Groups andbetween the Project Management Process●Project Integration Management is about:○Ensuring that the due dates of project deliverables, the project life cycle, and thebenefits realization plan are aligned;○Providing a project management plan to achieve the project objectives;○Ensuring the creation and the use of appropriate knowledge to and from theproject;○Managing project performance and changes to the project activities;○Making integrated decisions regarding key changes impacting the project;○Measuring and monitoring progress and taking appropriate action;○Collecting, analyzing and communicating project information to relevantstakeholders;○Completing all the work of the project and formally closing each phase, contract,and the project as a whole; and○Managing phase transitions when necessary
PM Process Group
: Initiation

PM Knowledge Area
: Stakeholders

What is a stakeholder?
- An individual, group or organization who may affect or be affected by a decision , activity or outcome of a project.
What does it do?
- Process of Identifying people or groups that can impact or be impacted by the project.
- Identify stakeholders early and analyse their importance, interests and stakes.
- Define a strategy to manage stakeholders.
Key Benefits
- Enables the project team to identify the appropriate focus for engagement of each stakeholder
ITTO

Inputs
1. Project Charter
- Identifies key stakeholders that are external and internal to the project.
2. Business documents
i. Business Case
- Identifies the project objectives and initial list of stakeholders
ii. Benefits Management Plan
- Documents how and when the benefits of the project will be delivered.
- May also identify the people/groups who will benefit from the delivery
3. Project Management Plan
i. Communication Management plan
- May include information about stakeholders
ii. Stakeholder ngagement plan
- Identifies management strategies and actions required to effectively engage stakeholders
4. Project Documents
i. Change Log
- May include a new stakeholder or change the nature of an existing stakeholder relationship to the project
ii. Issue Log
- Records issues that may introduce new stakeholders or change the type of participation of existing stakeholders
iii. Requirements documentation
- Provide information on potential stakeholders
5. Agreements
- Can contain references to other stakeholders
6. Enterprise Environmental Factors
- Factors that may impact our project but we lack an influence over these factors.
- This includes Government agencies, environment.
7. Operational Process Assets
- Process utilized to execute the project.
- This includes historic projects and stakeholder registers from these projects.
Tools & Techniques
1. Expert Judgement
- Experts help you identify a comprehensive list of stakeholders
2. Data Gathering
i. Questionnaires and surveys
- It is a mass information collection tool
ii. Brainstorming
- Gathering inputs from team members and SME’s
iii. Brain writing
- Participants are given questions ahead of brainstorming session.
3. Data Analysis
i. Stakeholder analysis
- To prepare a list of stakeholders with relevant information such as position in the organization, stakes, expectations, attitudes, interest
- Analyze positive and negative impact of each stakeholder
- This helps understand the project environment, reveal conflicts of interest, anticipate potential clashes, leverage existing relationships, Identify project champions.
- Process includes
- Identify Stakeholders
- Analyse and assess
- Classify and group
- Document
- Manage accordingly
ii. Document Analysis
- Assessing project documents and lessons learnt from previous projects to identify stakeholders
4. Data Representation
i. Stakeholder Grid
- Grouping stakeholders based on power, interest, influence
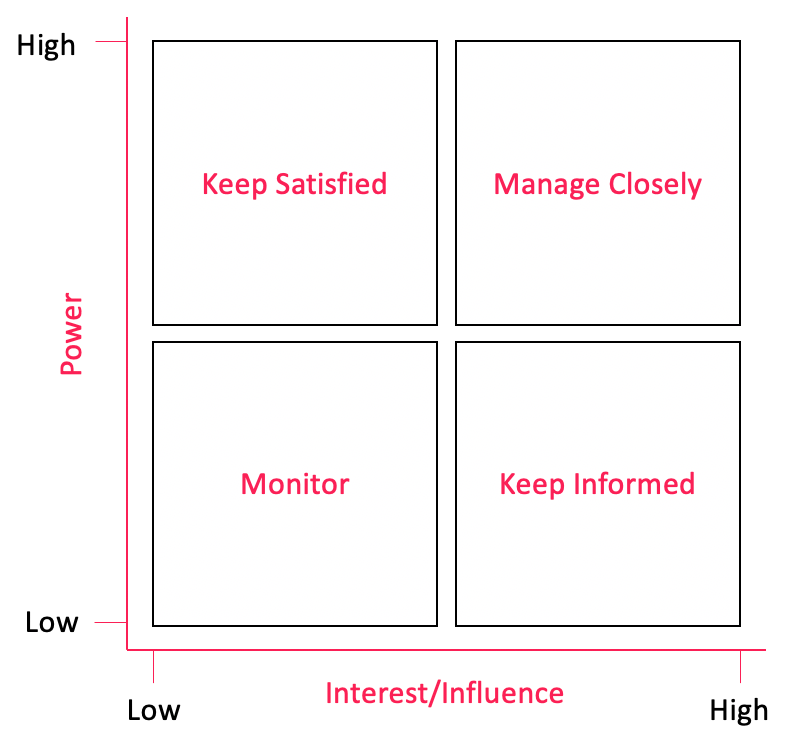
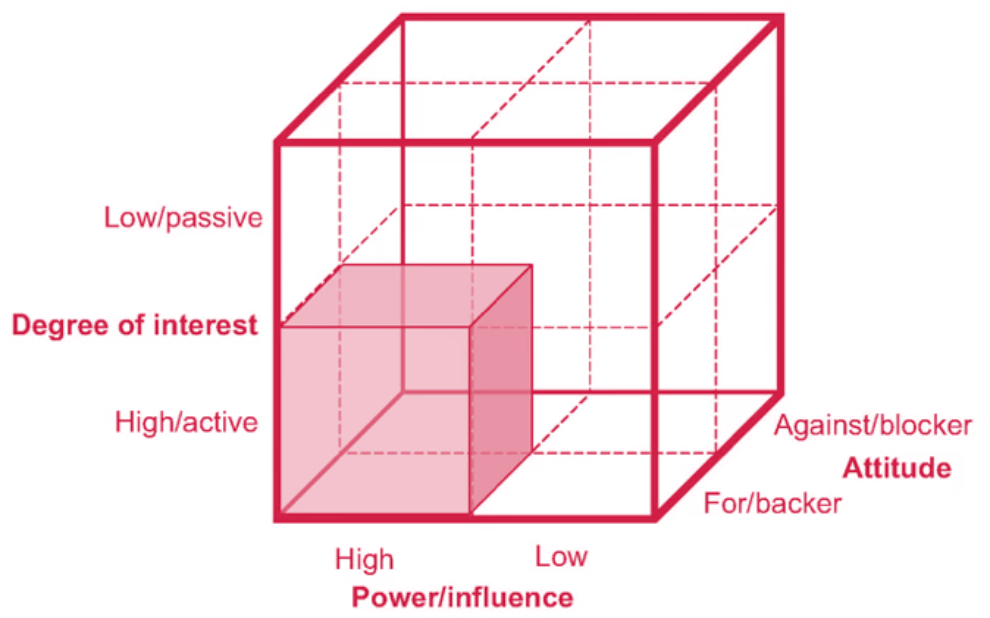
ii. Stakeholder Cube
- Three dimensional model to group stakeholders based on power, interest and attitude.
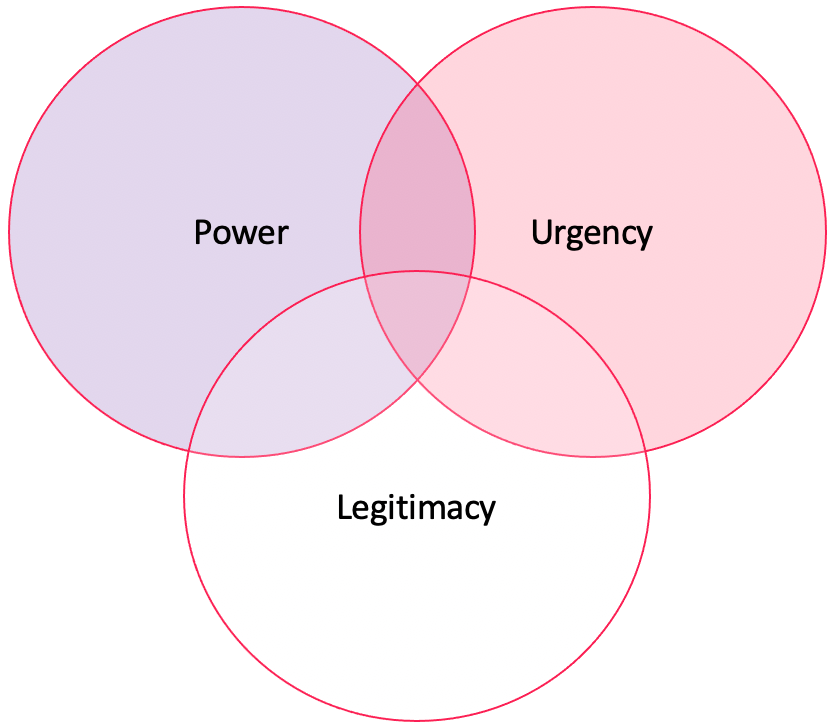
iii. Salience model
- Venn diagram that represents stakeholders in terms of their power, urgency and legitimacy (sometimes proximity)
iv. Directions of Influence
- Upward: Senior management or sponsors (above PM)
- Downward: People you are managing as PM
- Outward: Stakeholders outside your organization
- Sideward: Stakeholders that are on the same level as you

v) Prioritization
- Useful for large complex projects where stakeholders are changing frequently
5. Meetings
- To identify stakeholders and exchange information bout different stakeholders.
Outputs
1. Stakeholder Register
- Contains information about identified stakeholders
i. Identification information
- Name, position, location, contact details
ii. Assessment information
- Requirements, expectations, influence and project phase of interest
iii. Stakeholder classification
- Internal or external
- Supporter or neutral or resistor
- Impact or power
2. Change requests
- Can only implement after approval from Change Control Board (CCB)
3. Project Management Plan Updates
- Updated throughout the project lifecycle as more new stakeholders are known.
- Includes
- Requirements management plan
- Communications management plan
- Risk management plan
- Stakeholder engagement plan
3. Project Document Updates
- Includes
- Assumptions Log
- Issue log
- Risk Register
