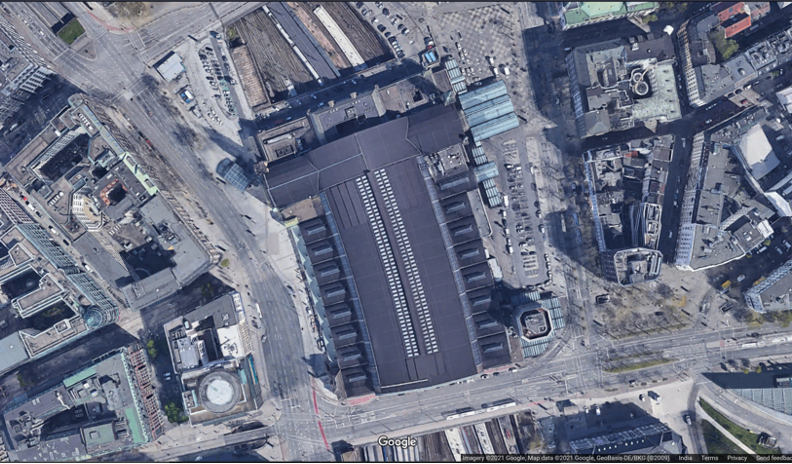
Hamburg Commercial Roof
LOCATION
Location
Hauptbahnhof,
20099 Hamburg, Germany
Co-ordinates
Lat: 53.5530
Lon: 10.0065
Elevation
16 m
55 m
DATA ACQUISITION (NATURAL RESOURCE)

Fig. 1: Hourly averaged daily DNI data (Y2021)

Fig. 2: Horizon and Sunpath

Fig. 3: Monthly DHI & GHI data (Y2021)
OTHER STATS
Specific photovoltaic power output
Yearly Global horizontal irradiation
Yearly Diffuse horizontal irradiation
Specific photovoltaic power output
Air Temperature
Optimum Tilt
Specific photovoltaic power output
Yearly Global horizontal irradiation
Yearly Diffuse horizontal irradiation
Specific photovoltaic power output
Air Temperature
Optimum Tilt
LOCATION SURVEY

Fig. 4: Dimensions of Project Site
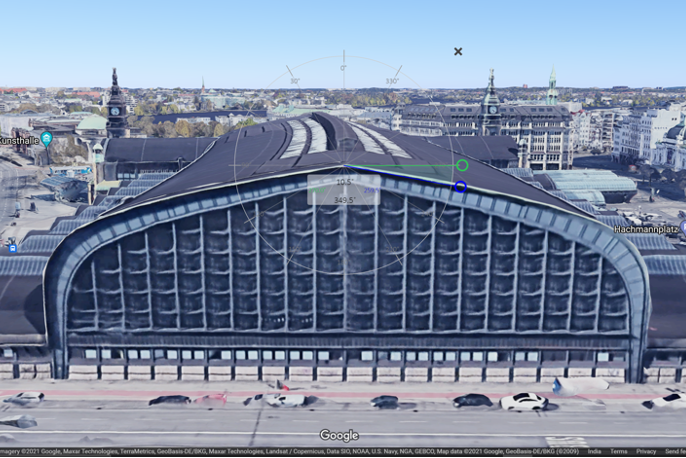

Fig. 5: Roof Tilt – 10o
Design
Major Components
PV Panels
For the first iteration, the choice for SunPower were made on the decision to choose a reputed Tier 1- Manufacturer. Mono-crystalline Modules were chosen as there is space restriction and to maximise energy output.
Selection of Modules are based on the following factors in the order of most to least importance:
- Cost
- Technology Type
- Efficiency
- Availability
- Warranty & Service Support



Inverter
An inverter is required to convert unregulated DC signals to regulated AC signals. A choice has to first be made between the two types of inverters i.e., string or centralised inverter. Since the project is not extremely large, string inverters are used instead of central inverters. These inverters have MPPT functionality and are less affected by shading. These types of inverters are also easier to maintain or replace.
A Fronius string inverter (Eco 25.0-3-S) with an MPPT tracker is chosen. Additionally, there is no requirement of combiner boxes as the chosen inverter has 6 DC input connections. Furthermore, it has 6 fuse holders which has to be equipped after accurate sizing.



Other Electrical Components Summary


Single Line Diagram
Premium Content 🔒
Fig. 8. 3D Shading Structure
Losses

3D Shading

Fig. 7. 3D Shading Structure

Fig. 8. Summary of all losses
Results
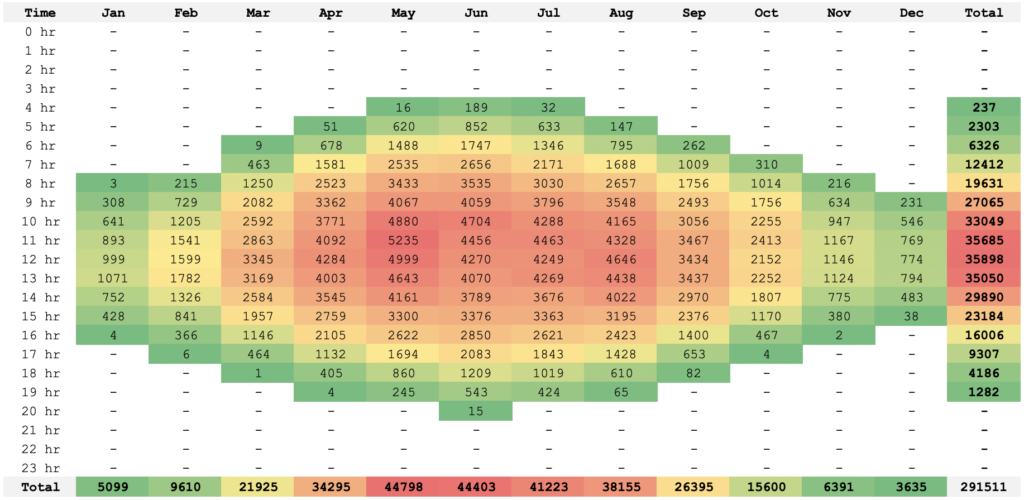
Fig. 9: Hourly Energy Production breakdown for the year (kWh)
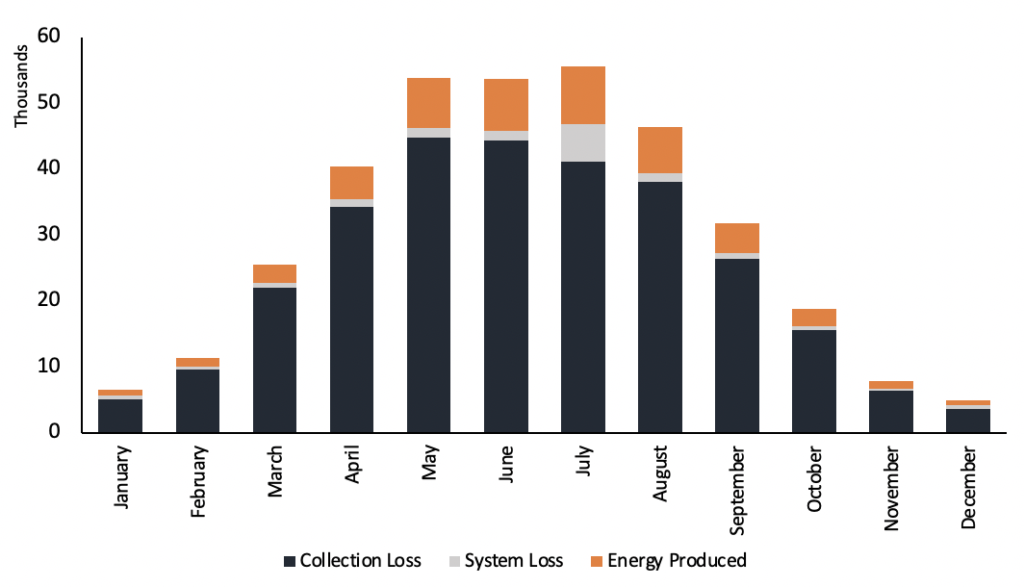
Fig. 10: Monthly Energy Production breakdown with Losses (kWh)

Fig. 11: Monthly Energy Production (kWh) with Performance Ratio (%)

Fig. 12: Daily Input/Output Diagram

Fig. 13. Daily System Output Energy
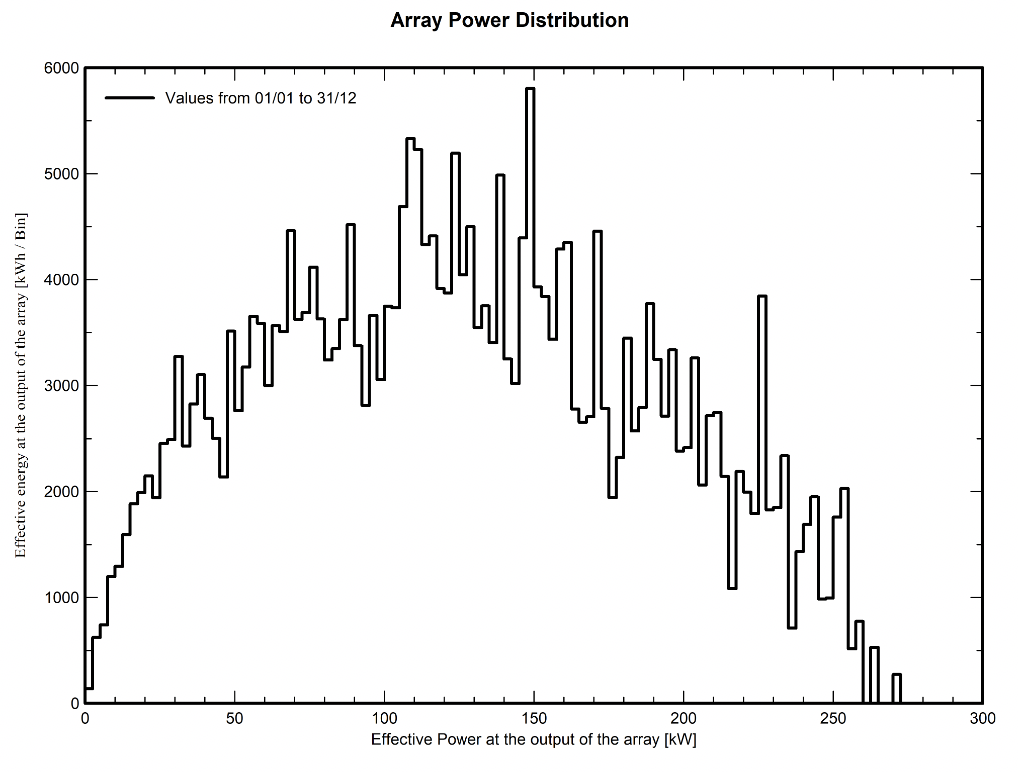
Fig. 14: Array Power Distribution

Fig. 15: Probability Distribution Results (P50, P75 & P90)
ECONOMIC ANALYSIS

Fig. 16: Breakdown of costs (USD)
A cash flow is drawn by combining the various costs (Hardware, Installation, Soft Costs & OPEX) along with the cost offset (revenue) by supplying part of the electricity requirements. The Capital investment associated with the construction phase is fully made in Y 1. The plant moves on to the operational phase at the beginning of Y 2 and continues operating for the next 25 years i.e. till Y 26. Finally, at the end of the lifespan of the plant (Y 27), where the plant is decommissioned.

Table. 1: Costs & KPI

Fig. 17: Cumulative Cash Return graph
Interested to know more?
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is a power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system.
It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system’s overall performance and include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). As PV systems convert light directly into electricity, they are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling.
PV systems range from small, rooftop-mounted or building-integrated systems with capacities from a few to several tens of kilowatts, to large utility-scale power stations of hundreds of megawatts. Nowadays, most PV systems are grid-connected, while off-grid or stand-alone systems account for a small portion of the market.
Operating silently and without any moving parts or environmental emissions, PV systems have developed from being niche market applications into a mature technology used for mainstream electricity generation. A rooftop system recoups the invested energy for its manufacturing and installation within 0.7 to 2 years and produces about 95 percent of net clean renewable energy over a 30-year service lifetime.[1]:30[2][3]
Due to the growth of photovoltaics, prices for PV systems have rapidly declined since their introduction. However, they vary by market and the size of the system. In 2014, prices for residential 5-kilowatt systems in the
United States were around $3.29 per watt,[4] while in the highly penetrated German market, prices for rooftop systems of up to 100 kW declined to €1.24 per watt.[5] Nowadays, solar PV modules account for less than half of the system’s overall cost,[6] leaving the rest to the remaining BOS-components and to soft costs, which include customer acquisition, permitting, inspection and interconnection, installation labor and financing costs.[7]:14
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is a power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system.
It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system’s overall performance and include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). As PV systems convert light directly into electricity, they are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling.
PV systems range from small, rooftop-mounted or building-integrated systems with capacities from a few to several tens of kilowatts, to large utility-scale power stations of hundreds of megawatts. Nowadays, most PV systems are grid-connected, while off-grid or stand-alone systems account for a small portion of the market.
Operating silently and without any moving parts or environmental emissions, PV systems have developed from being niche market applications into a mature technology used for mainstream electricity generation. A rooftop system recoups the invested energy for its manufacturing and installation within 0.7 to 2 years and produces about 95 percent of net clean renewable energy over a 30-year service lifetime.[1]:30[2][3]
Due to the growth of photovoltaics, prices for PV systems have rapidly declined since their introduction. However, they vary by market and the size of the system. In 2014, prices for residential 5-kilowatt systems in the
United States were around $3.29 per watt,[4] while in the highly penetrated German market, prices for rooftop systems of up to 100 kW declined to €1.24 per watt.[5] Nowadays, solar PV modules account for less than half of the system’s overall cost,[6] leaving the rest to the remaining BOS-components and to soft costs, which include customer acquisition, permitting, inspection and interconnection, installation labor and financing costs.[7]:14
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is a power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system.
It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system’s overall performance and include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). As PV systems convert light directly into electricity, they are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling.
PV systems range from small, rooftop-mounted or building-integrated systems with capacities from a few to several tens of kilowatts, to large utility-scale power stations of hundreds of megawatts. Nowadays, most PV systems are grid-connected, while off-grid or stand-alone systems account for a small portion of the market.
Operating silently and without any moving parts or environmental emissions, PV systems have developed from being niche market applications into a mature technology used for mainstream electricity generation. A rooftop system recoups the invested energy for its manufacturing and installation within 0.7 to 2 years and produces about 95 percent of net clean renewable energy over a 30-year service lifetime.[1]:30[2][3]
Due to the growth of photovoltaics, prices for PV systems have rapidly declined since their introduction. However, they vary by market and the size of the system. In 2014, prices for residential 5-kilowatt systems in the
United States were around $3.29 per watt,[4] while in the highly penetrated German market, prices for rooftop systems of up to 100 kW declined to €1.24 per watt.[5] Nowadays, solar PV modules account for less than half of the system’s overall cost,[6] leaving the rest to the remaining BOS-components and to soft costs, which include customer acquisition, permitting, inspection and interconnection, installation labor and financing costs.[7]:14
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is a power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system.
It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system’s overall performance and include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). As PV systems convert light directly into electricity, they are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling.
PV systems range from small, rooftop-mounted or building-integrated systems with capacities from a few to several tens of kilowatts, to large utility-scale power stations of hundreds of megawatts. Nowadays, most PV systems are grid-connected, while off-grid or stand-alone systems account for a small portion of the market.
Operating silently and without any moving parts or environmental emissions, PV systems have developed from being niche market applications into a mature technology used for mainstream electricity generation. A rooftop system recoups the invested energy for its manufacturing and installation within 0.7 to 2 years and produces about 95 percent of net clean renewable energy over a 30-year service lifetime.[1]:30[2][3]
Due to the growth of photovoltaics, prices for PV systems have rapidly declined since their introduction. However, they vary by market and the size of the system. In 2014, prices for residential 5-kilowatt systems in the
United States were around $3.29 per watt,[4] while in the highly penetrated German market, prices for rooftop systems of up to 100 kW declined to €1.24 per watt.[5] Nowadays, solar PV modules account for less than half of the system’s overall cost,[6] leaving the rest to the remaining BOS-components and to soft costs, which include customer acquisition, permitting, inspection and interconnection, installation labor and financing costs.[7]:14
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is a power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system.
It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system’s overall performance and include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). As PV systems convert light directly into electricity, they are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling.
PV systems range from small, rooftop-mounted or building-integrated systems with capacities from a few to several tens of kilowatts, to large utility-scale power stations of hundreds of megawatts. Nowadays, most PV systems are grid-connected, while off-grid or stand-alone systems account for a small portion of the market.
Operating silently and without any moving parts or environmental emissions, PV systems have developed from being niche market applications into a mature technology used for mainstream electricity generation. A rooftop system recoups the invested energy for its manufacturing and installation within 0.7 to 2 years and produces about 95 percent of net clean renewable energy over a 30-year service lifetime.[1]:30[2][3]
Due to the growth of photovoltaics, prices for PV systems have rapidly declined since their introduction. However, they vary by market and the size of the system. In 2014, prices for residential 5-kilowatt systems in the
United States were around $3.29 per watt,[4] while in the highly penetrated German market, prices for rooftop systems of up to 100 kW declined to €1.24 per watt.[5] Nowadays, solar PV modules account for less than half of the system’s overall cost,[6] leaving the rest to the remaining BOS-components and to soft costs, which include customer acquisition, permitting, inspection and interconnection, installation labor and financing costs.[7]:14
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is a power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system.
It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system’s overall performance and include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). As PV systems convert light directly into electricity, they are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling.
PV systems range from small, rooftop-mounted or building-integrated systems with capacities from a few to several tens of kilowatts, to large utility-scale power stations of hundreds of megawatts. Nowadays, most PV systems are grid-connected, while off-grid or stand-alone systems account for a small portion of the market.
Operating silently and without any moving parts or environmental emissions, PV systems have developed from being niche market applications into a mature technology used for mainstream electricity generation. A rooftop system recoups the invested energy for its manufacturing and installation within 0.7 to 2 years and produces about 95 percent of net clean renewable energy over a 30-year service lifetime.[1]:30[2][3]
Due to the growth of photovoltaics, prices for PV systems have rapidly declined since their introduction. However, they vary by market and the size of the system. In 2014, prices for residential 5-kilowatt systems in the
United States were around $3.29 per watt,[4] while in the highly penetrated German market, prices for rooftop systems of up to 100 kW declined to €1.24 per watt.[5] Nowadays, solar PV modules account for less than half of the system’s overall cost,[6] leaving the rest to the remaining BOS-components and to soft costs, which include customer acquisition, permitting, inspection and interconnection, installation labor and financing costs.[7]:14




